As climate change progresses, droughts are becoming more frequent and more severe. They affect crops and livestock, and are a threat to the food supply. They also can cause water scarcity, which can lead to public and environmental health problems.
Droughts are common in many different areas. They can last for a year, decades or even centuries. They can also be very severe, ranging from mild to extremely serious. A drought is defined as a situation where there is insufficient precipitation over a long period. Drought can occur for many reasons, including human activity and dry weather. These and other factors can have a negative impact on crop yields, as well as the production process.

Droughts can be a natural occurrence or caused by a human-generated greenhouse gas emission. The latter is more prevalent and is associated to higher temperatures, less rainfall and the evaporation.
Plants can't retain moisture if there isn't enough rainfall. This reduces the water availability for crops in warmer months. Low moisture can cause trees and shrubs to die, rangelands to become saline and wildlife to die. Wildfires can cause severe damage because the vegetation has no place else to go. Research suggests that climate change could be contributing to the increase in droughts.
The likelihood of drought is rising due to shifting weather patterns and higher ocean temperatures. Storms, for example, are moving closer to the poles. The Gulf of Mexico is heating and the jet stream is moving to the south. This causes moisture in the Gulf to move to the Great Plains. However, these changes have not yet been adequately analyzed.
Another study revealed that the likelihood of droughts co-occurring in the 21st century increased significantly. These simultaneous droughts could have catastrophic consequences for global food safety. The impact on agricultural output could be severe, and the price of food can increase.

While droughts are unpredictable, scientists have a high degree of confidence that they will increase as a result of climate change. The Palmer Drought Severity Index predicts future drought for 70% of the earth's land. As a result, this number will increase by 1.7x.
Droughts are more severe in developing countries, especially Latin America. Low rainfall is causing crop damage. In addition, underground aquifers are draining their water faster than it is refilling, which can lead to further destruction of crops. This has driven farmers from their land. Many have witnessed political unrest as well as food riots.
Globally, there's been a noticeable increase in drought severity. Human-generated warming and fossil fuel use are key contributors. For example, according to a recent study, 46% of the increase in severity of droughts is attributed to human-generated warming.
If we continue to produce more carbon dioxide, the atmospheric concentration of greenhouse gases will rise further. This will make drought even more dangerous. Researchers have been careful to note that the connection between human-generated warming and droughts is not absolute, and that other factors also contribute to the occurrence of droughts.
FAQ
How can the world move towards a more sustainable future in light of the challenges posed by climate change?
Sustainability refers to the ability to satisfy current needs while not compromising future generations' ability to do so. An urgent need exists to act to eliminate our dependency on finite natural resources and to shift towards a more sustainable method of using them.
To move towards a more sustainable future, it is important for us to reconsider our current models of consumption and production, as well as our dependence on natural resources such as fossil fuels. We must look for new technologies and renewable sources of power, as well as systems that lower harmful emissions and still provide our daily needs.
It is important to adopt an integrated approach to sustainability. This means that all aspects are considered, including the materials used, waste management strategies and reuse strategies, as well energy usage in transportation and industry. There are many potential solutions available including the utilization renewable energies like sun, wind, and water power; improved waste management systems; higher efficiency in agriculture; improved transport network; green building regulations; sustainable urban planning initiatives.
We need behavioral changes to reach this goal across society. Education programs are required to educate people about climate change and show them how they can help create a more sustainable future.
Ultimately, only through collaboration between governments, industry leaders, and citizens will we be able to make significant progress in creating a more sustainable world for generations to come.
What impact does politics have on global efforts to tackle climate change?
Climate change has become a highly politicized topic that has caused great divisions among governments, nations, and individuals. The political positions of various actors have an effect on the implementation and effectiveness of measures to combat climate change. It has become difficult to find consensus on global efforts to tackle this pressing environmental crisis.
The overwhelming majority of scientists agree with the fact that human-generated global warming is real. It is urgent for action to address it. These issues are often subject to political interference that can hamper global cooperation in order to implement sustainable energy practices, preserve natural habitats, find viable technological solutions and other interventions related to climate change.
Most governments are eager to protect their business interests and enforce rules that will limit business activity as much as possible. This is often in conflict with the regulations experts recommend to combat climate change. Without strong commitments from all participating countries and wide-scale international action, it becomes very difficult for any single state or group of states to adequately address climate change through legislation or otherwise.
Different power dynamics can make it difficult to achieve full consensus on the best ways to address climate change. Countries with more economic power frequently appoint their own representatives for international negotiations over the environment. This can lead lopsided discussions between countries' perceived interests and those of all other parties. The potential side effects of radical change like geoengineering, have been extensively discussed at both the national level and internationally.
At a grassroots level too, grassroots movements have struggled against powerful opponents including corporate ownerships and well-funded lobbies trying to maintain politically favorable positions for their industries especially when it comes to funding research into alternative forms of energy production or enforcing renewable energy technology mandates such as low emissions targets for vehicles etcetera - meaning individual governments must remain clearheaded about potential rewards and outcomes if they are going actively try to make valid progress on the matter in the question itself instead seeking public favor through short-term gains or even spectacles.
A coordinated effort to reduce our environmental crisis will only succeed if resources are distributed properly and there is no political divide between nations.
What are the impacts of climate change and global warming on agriculture and food security
Climate change and global warming have a direct impact on agriculture and food security. Changes in climate can have an impact on rainfall patterns, temperature, soil moisture, extreme weather, and other aspects of agriculture. This can cause disruptions in farming, decrease crop yields, and result in a loss of agricultural biodiversity. Warmer temperatures can cause crop diseases and pests to multiply. It can also affect the ranges that are suitable for agricultural production. This can result in higher costs for food production, and worsening hunger and nutrition around the world.
Rising sea levels are a threat as they could flood important agricultural land along the coast. This would lead to an increase in salinity in wetlands that support important crops. Livestock production is similarly affected by the changing climate - high temperatures during summer months can reduce fertility rates for animals like cattle, sheep, and goats, resulting in lower milk yields which exacerbate food insecurity across communities.
The relationship between climate change and global warming is a complex one; however, efforts are being made to mitigate these results through adaptation strategies implemented by governments worldwide such as strategic investments in climate-smart agriculture (CSA). This includes promoting sustainable methods like crop rotation techniques and genetic diversity through conservation of native seed varieties. These help to protect against adverse impacts from extreme weather conditions and other environmental stressors due to the changing climate. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
Farmers around the globe must adopt technology that is more sensitive to climate changes to ensure food security in a changing environment. There must be improvements made to existing infrastructure in order to take the appropriate actions when critical crop thresholds fall. This includes installing stable irrigation networks that provide adequate access water at times when it is difficult for farmers to grow crops. For sustainable solutions to be created that will ensure the continued compliance with international dietary guidelines in our ever-changing climates, it is necessary to have a cohesive collaboration among all stakeholders. This includes government officials at international levels as well as NGOs located at local communities.
What can we do to limit or mitigate the impacts of climate change?
There are various measures that can be taken to reduce and mitigate the effects of climate change. These include reducing greenhouse emissions by using greener energy sources and better energy practices. It's important that people are educated about climate change. This encourages them to take responsibility for their actions.
How does human activity contribute to climate change?
Climate change is due in large part to human activity. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. (IPCC), human activity is responsible for more that 70% of all global warming.
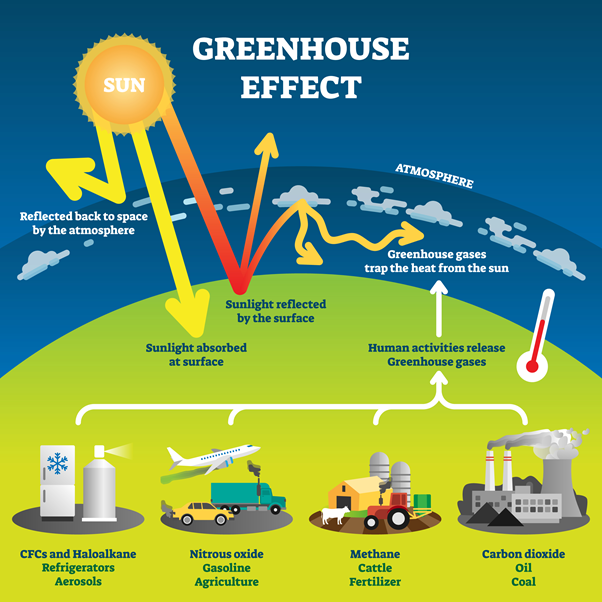
Burning Fossil Fuels: Burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This adds to already existing levels of atmospheric CO2, which act as a "greenhouse gas" by trapping heat from the sun in Earth's atmosphere and increasing temperatures even further. This can result in an increase in ocean levels due to Arctic ice melting. This creates unpredictable weather patterns that can disrupt food production and threaten human health.
Deforestation is the removal of trees that store atmospheric carbon dioxide in their trunks. This happens when they use it during photosynthesis. Cutting down forests also increases albedo - the amount of reflected solar radiation coming back into space - reducing solar heat absorption by the earth's surface thus promoting excessive warming at the global level. Also, deforestation can lead to a decrease in local air quality and respiratory problems.
Farming is responsible for 14% to 18% of all anthropogenic greenhouse emissions globally each year. Animal waste releases large amounts of methane gas into the atmosphere due to its composition rich in methane bacteria Eating less or no animal products altogether can be an effective way to reduce your contribution towards global warming from this source alone., Agriculture itself also relies heavily on fertilizers which contain nitrous oxide released into our atmosphere directly harms humans creating smog from ground level ozone harming our respiratory system making polluted air hazardous for life.
In conclusion, while human activity has had an adverse impact on our environment for centuries, technological advances have made it possible to turn our attention towards the future. We can leverage technology through green innovation to help us move forward in our efforts to reduce climate change and keep everyone safe.
What are the international efforts currently being made to address climate change
The international effort to tackle climate change has reached a new level of unity and momentum. Countries around the world are increasingly collaborating on ways to reduce emissions, strengthen resilience against impacts, and invest in renewable energy sources.
At the global level, the Paris Agreement has galvanized collective action and serves as a framework for individual countries to set voluntary targets for reducing emissions. The UN Framework Convention on Climate Change and (UNFCCC) provides political guidance, as well as piloting initiatives such a carbon market.
Other regions are seeing progress. The European Green Deal is a comprehensive legislation package that seeks to create a European economy with sustainability as its core. Countries on the African continent also have committed to The African Renewable Energy Initiative, which aims increase Africa's participation in global renewable energy production.
Along with policy changes, action can be observed across all sectors and industries. Cities are actively moving toward sustainable public transport systems. Society as a whole is moving towards more sustainable lifestyles. Companies invent technologies that reduce carbon emissions. Investors are shifting their capital away to renewables.
The OECD committee represents wealthy countries and has established common standards for reporting national climate action through the Common Reporting Framework, also called the 2021 Guidelines.
All of these efforts show an unprecedented focus on climate action. To meet climate goals, both governments and civil society must continue to build on the momentum.
Statistics
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to Educate your Community about Climate Change and Mobilize Action
You can learn about climate change through many different methods, from interactive online tools and educational resources to classroom activities and simulations to experiential learning programs and classroom activities. The following key elements are essential for effective climate change education
-
Practical knowledge of the subject is essential for people to be able to make informed decisions.
-
demonstrating ways that individuals can make a difference
-
Engaging participants in an open discussion about possible solutions
-
Shared experiences inspire action
By providing comprehensive climate change lessons for both students and adults alike, educators will be able to help their communities develop strategies for reducing their environmental footprint.
It is also possible to connect scientific research with real-world examples, which can be a unique way of engaging audiences in meaningful dialogue. Participants also have the opportunity to observe positive outcomes and learn from them, which can lead to further innovation or replication within their organizations.
Participants are empowered by incorporating action-oriented activities in educational curriculums. This gives them the mental tools needed to create campaigns, petitions, and take local actions. It also allows them to be agents for social and political change or sustainability improvement initiatives. In addition, individual agency emphasizes the importance of participating in reducing emissions. It also shows participants' collective contributions to a greater outcome. A key element in policy-making is to involve stakeholders as early as possible. This encourages their active involvement at every stage of the process and could result in better outcomes for all. Through concerted efforts at increasing public understanding of the impacts of climate change coupled with taking appropriate action on mitigating greenhouse gas emissions, we might be able to create an environment where these pressing matters are addressed urgently with attention applied where necessary most so that together we may one day be able to ensure successful implementation measures that will help us reach our collective goals out ahead time as well.