Global climate change is a serious topic that affects the lives of all people on the planet. Scientists have studied the impacts of this phenomenon in numerous ways. These impacts include changes in weather patterns and the loss of biological diversity. It is essential that governments take steps to mitigate the effects of this trend.
In order to provide a broad picture of the current global research on climate change, a bibliometric study was conducted. This study compares the scientific output of different countries to identify the most significant aspects of the topic. This was done by evaluating a 40,062 article database on climate change. These articles were taken directly from the World of Science data base. The comprehensive assessment of the current state of the art was possible through the analysis of publications that were based on technological, ecological, and socioeconomic factors.
Researchers found that the ocean heat content has increased significantly over the past decade. Additionally, the Arctic is heating up more than twice as fast as the rest of the world. As a result, sea levels are rising rapidly. As a consequence, the worst-affected areas of the climate change are those closest to coastal ecosystems and the cities with the greatest populations.
While scientists have analyzed a number of different factors influencing the Earth's energy balance, they have also used sophisticated models to predict the future of the climate. These models reveal that the developing countries are facing a heavy burden of climate impacts. However, these models can not reproduce what has actually occurred. Hence, reliable estimation of the changes caused by climate change is the heart of research.
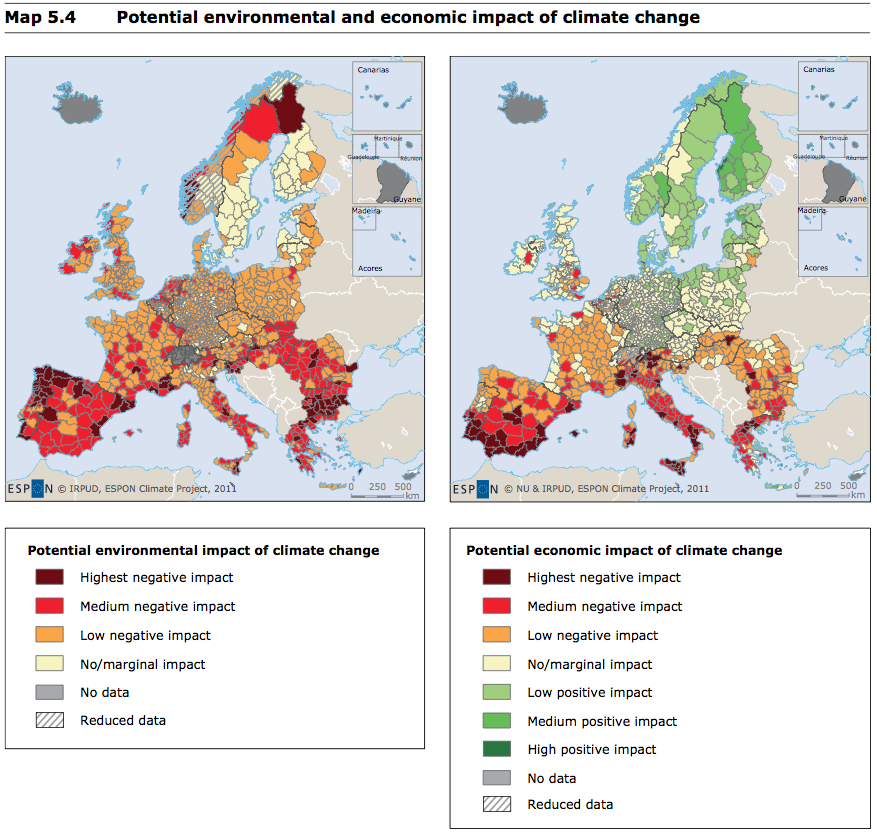
While there is a lot evidence that supports global warming, scientists still have difficulty estimating the true impact of the phenomenon. All mitigation strategies need to base themselves on an accurate estimate of the climate change's impacts. The Global Climate Risk Index gives data about the severity of weather events over various years.

The rate at which greenhouse gases concentrations are increasing is another indicator of global climate changes. Research has shown that the rate at which greenhouse gas concentrations have increased over the last century is unprecedented. Because of human activities, the atmospheric concentrations have increased. Therefore, these gases trap more of the Sun's heat. According to research, the rate of warming over the past century is 10 times faster than the rate of warming over the last decade.
Other signs that the earth is undergoing a rapid change include melting ice sheets and increasing heat in the ocean. These changes could have devastating consequences for human life, including our food supply and water supply. Already, signs are emerging that climate change will lead to an increase in extreme weather events. Despite numerous warning signs of a changing climate and the need to act, governments are yet to do anything to address its effects.
FAQ
How do climate change and global warming impact agriculture and food security?
Climate change and global warming are directly impacting agriculture and food security. Changes in climate can have an impact on rainfall patterns, temperature, soil moisture, extreme weather, and other aspects of agriculture. This can disrupt farming activities, reduce crop yields and lead to losses of agricultural biodiversity. Warmer temperatures could lead to the growth of pests or diseases, which can have a negative impact on crops. This can increase food production costs, as well as cause hunger and other nutritional problems worldwide.
Rising sea levels are a threat as they could flood important agricultural land along the coast. This would lead to an increase in salinity in wetlands that support important crops. Livestock production is similarly affected by the changing climate - high temperatures during summer months can reduce fertility rates for animals like cattle, sheep, and goats, resulting in lower milk yields which exacerbate food insecurity across communities.
Global warming and climate change are complex issues. However, governments around the world are making efforts to reduce these effects through adaptation strategies such as climate-smart agricultural (CSA) strategic investments. This involves promoting sustainable methods such as crop rotation techniques or genetic diversity through the conservation of native seed varieties, which help protect against negative impacts from extreme weather conditions or other environmental stressors caused by the changing climate. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
In order to ensure food safety in an ever-changing environment, farmers across the globe will need to use technologies that are more sensitive and adaptable to changing climates. Existing infrastructure must be improved to allow for the appropriate action when necessary. This includes stabilizing irrigation networks that have adequate access to water during periods when there are less water sources due either to extreme downpours or warmer climates. It is essential to create sustainable solutions that adhere to the international guidelines for quality nutrition in our changing climates. This requires collaboration between all stakeholders, from government agencies at an international level to local NGOs.
How does climate change politics impact global efforts?
Climate change is a hotly debated issue, which has led to a lot division among countries, governments, as well as individuals. The implementation of measures to address climate change is affected by the political stances of various actors. It has become difficult to find consensus on global efforts to tackle this pressing environmental crisis.
A majority of scientists agree that climate change caused by humans is real and must be addressed immediately. These politics often hamper global cooperation needed to achieve effective progress in implementing sustainable energy practices.
Many governments around the globe want to protect business interests and enforce policies that restrict business activities. This often clashes with regulations that experts recommend for effectively addressing climate change. Without strong commitments by all countries involved and large-scale international action it is difficult for any state or group to adequately address climate changes through legislation.
Further complicating the process of reaching full agreement on how to deal with climate change is the differences in power dynamics. Countries with more economic power frequently appoint their own representatives for international negotiations over the environment. This can lead lopsided discussions between countries' perceived interests and those of all other parties. At both the national and international level, there have been extensive discussions about potential side effects of radical changes like geoengineering.
Also at the grassroots level, grassroots movements have fought against powerful opponents such as corporate ownerships. These lobbies are trying to preserve politically favorable positions for their industry especially when it is about funding research into alternative sources of energy production or enforcing Renewable Energy Technology mandates. If individual governments want to make valid progress in the subject matter themselves instead of seeking short-term benefits or spectacles, they must be clearheaded about possible outcomes.
A coordinated effort to reduce our environmental crisis will only succeed if resources are distributed properly and there is no political divide between nations.
How are developing countries and communities affected by climate change?
Developing countries and communities are particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change due to limited access to resources, healthcare systems, and technology. Changes in temperature, precipitation, and sea levels increase pressure on already scarce resources, with floods and droughts wearing away at already fragile ecosystems. Rising temperatures can cause a drop in crop yields which will adversely impact the poorer communities that are struggling to feed their families. Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and heatwaves, can cause the destruction of infrastructures and displacement of people, which further perpetuates economic inequality.
Climate change will have long-term effects on resources, poverty, and health. This includes an increase in the number of vector-borne disease such as dengue fever or malaria. In addition, there will be a higher risk of flooding due to rising sea levels coupled with extreme weather events putting lives at risk in coastal areas where populations often lack the adequate infrastructure or emergency services needed for evacuation. While mitigating greenhouse gases is essential to build resilience to these risks, there are other options available. These include better management of freshwater resources and easier access for health facilities. This helps with the prevention of diseases such as malaria.
How can we address climate change by addressing the role of the energy industry?
The importance of the energy industry in climate change mitigation is enormous. The main source of global warming comes from the burning of fossil energy. It releases carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, traps heat, and results in an increase on Earth's average temperature.
Energy sources must shift away from fossil-emitting energy sources like coal and natural gases and towards renewable energy sources like wind, solar and geothermal to address this problem. This can be achieved through incentives and government policies, but also by investing in new technology like hydrogen fuel cells. Businesses and households can reduce their carbon emissions by investing in infrastructure to support the use of renewable energy sources.
Another option is to move away from polluting transport options such as petroleum-fueled vehicles and towards electric cars or public transport. Governments have great power to lead societies' transitions away from oil-based infrastructures by supporting research into battery technologies and incentivizing consumers to invest in cleaner modes of transportation.
In order to reduce their carbon footprint, companies need to adopt green business methods. These include installing better insulation systems in offices and creating energy efficiency plans for manufacturing facilities. This can dramatically reduce operational costs, while improving environmental performance metrics.
These initiatives must be championed not just at the company level but also at the government level for them to be truly effective; increasing taxes on pollution products encourages individuals to switch away from harmful practices without forcing them financially outcompeting polluters by providing vouchers or subsidies for low-carbon products will create an ongoing market to support sustainability efforts moving forward. The private and public sector must work together to combat climate change. Providing vouchers or subsidies for low-carbon products and switching to cleaner energy sources will create a market that supports sustainability efforts.
How does human activity affect climate change
Human activity is one of the major factors contributing to climate change. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change(IPCC) states that humans are responsible more than 70% for global warming in the past 20 years.
Burning fossil fuels: Carbon dioxide is produced when fossil fuels, such as oil and coal, are burned. This raises the already existing atmospheric levels of CO2 which acts as an "greenhouse gas", trapping heat from Earth's surface and increasing temperatures. This can result in an increase in ocean levels due to Arctic ice melting. This creates unpredictable weather patterns that can disrupt food production and threaten human health.
Deforestation is the removal of trees that store atmospheric carbon dioxide in their trunks. This happens when they use it during photosynthesis. Also, cutting down forests can increase albedo - which is the amount reflected solar radiation going back into space. It also reduces solar heat absorbtion by the earth's surfaces and encourages excessive global warming. Also, deforestation can lead to a decrease in local air quality and respiratory problems.
Farming: Between 14% and 18% of global anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions are attributed to animal agriculture each year. Because of its high methane content, animal waste emits large amounts methane into the atmosphere. Reducing your intake of animal products is an effective way to lower your greenhouse gas emissions. Nitrous oxide can also be released into our atmosphere. This creates smog that harms our respiratory system.
In conclusion, although human activity has had a devastating impact on our environment for centuries, technological advancements have enabled us to focus our minds towards the future. Instead of relying on carbon-emitting heavy industry, we can use green innovation to create eco-friendly efforts that combat climate change effectively and ensure everyone's safety.
What is the current climate like? How is it changing?
The current climate is characterized by unprecedented uncertainty and change. Unprecedented levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide are causing temperatures to increase significantly, leading to droughts, heat waves, changing rainfall patterns, melting polar ice caps, ocean acidification, and rising sea levels.
These changes already have a profound effect on ecosystems all over the globe, causing habitat destruction and extinctions. They are also threatening the lives and livelihoods of billions of people, particularly those in areas already facing resource scarcity and poverty.
Increased average surface temperatures, which are caused by human activity, have led to an increase of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes or cyclones. As temperatures continue their climb, this trend is expected to continue.
The effects of a rapidly changing global climate can be felt everywhere from rising food insecurity to displacement from extreme weather events or sea level rise forcing communities to relocate. Climate change is also contributing to existing social inequalities. Itdisproportionately affects marginalized communities, which lack the resources and knowledge required to adapt.
While progress has been made in some countries in terms of reducing carbon emission or developing renewable energy programs, there has yet to be any meaningful action taken at a global scale that would allow us to address these issues effectively. In order for us to prevent further disruption and devastation from climate change all nations must come together and take urgent action now while at the same time planning for adaptation in an increasingly uncertain world.
Statistics
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
External Links
How To
How to Reduce your Carbon Footprint and Fight Climate Change
There are many steps that you can take to reduce your carbon footprint and help fight climate change. First, you can reduce your energy consumption by purchasing energy-efficient appliances, lighting and insulation. You can also reduce energy consumption by turning down your thermostat during winter and summer, unplugging electronics, using public transportation, walking instead of driving, and switching off lights when they are not in use.
Second, make sure to recycle materials whenever possible and compost food scraps instead of throwing them away so they don't end up in landfills where they release methane gas into the atmosphere. Third, plants trees around your house for shade and natural cooling. The air absorbs carbon dioxide through the vegetation. The last thing you should do is to look for products that have minimal packaging and sustainable labels, such organic cotton or FSC certified wood. This means the product has been sustainably managed over time in order to maintain forest health.
Apart from reducing your own emissions, you can also help organizations like Emissions Reduction Alberta and Climate Change Solutions. The Nature Conservancy Canada works towards reducing emissions through clean energie investments and international initiatives such as ICLEI - Local Governments for Sustainability.
Making small changes in our daily lives can help us all fight climate change together.