The term "climate crisis" has become synonymous with the dangers of global warming. It has been used to call for aggressive climate change mitigation. However, the climate crisis isn't just about climate change. It's also about how people choose to respond. This has a significant psychological impact.
Climate in Crisis examines the effects of climate change and global warming on individuals, communities and the planet. It examines the way in which Indigenous communities are affected by climate changes.
Many environmental activists are protesting climate change's impact on extreme weather events as it leads to more of them. Some of these people are scientists and activists. Others are farmers who are beginning to adopt more sustainable practices.
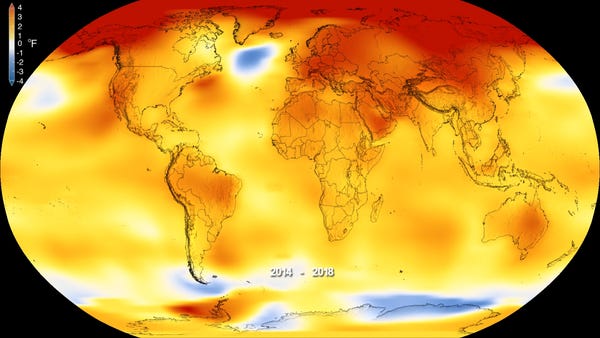
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Earth's climate is rapidly changing. And if we don't act, we could see an increase in extreme heat, heavy precipitation, and drought. Even the planet's ocean levels are increasing. These changes can not be reversed.
The most vulnerable are pastoralists who live in rural areas and nomadic communities. The Northern Triangle of Central America (El Salvador-Guatemala, Guatemala, Honduras and Mexico) has seen droughts and floods increase in recent years. These conditions have affected rural economies and caused floods. Without adequate action on emissions, 75,000 people in Kenya may face riverine flooding in 2030.
Experts also predict an increase in suicide and substance abuse as a result climate change. The ACA Climate Change Task Force has reported that climate change trauma affects people more severely in disadvantaged groups.
Climate in Crisis also discusses the effects of environmental colonialism upon Indigenous people. In Panama, Indigenous communities were forced to face deforestation and logging and the displacement of their people from their ancestral homelands.
Costa Rica's urban growth has been accompanied with concern for sustainability and conservation. Many environmental activists believe that the media hasn't done enough to highlight this issue. However, several tactics have been recommended for improving the media's communications on the climate issue.

Researchers from the Political Psychology Research Group studied several Americans in an effort to understand the significance of the climate crisis. Most Americans believe that Earth is warming. It is also a serious problem according to 85% of respondents. However, almost half the respondents doubted that the warming was caused by human activity.
Despite all this, most respondents believed that climate change was real and is a result human action. While the political debate may have moved, the public's attitude on climate matters has not. However, technology is still lacking to address the climate crisis.
In some cases, the false balance can sneak into the story through soundbites and failure to analyze. The majority of issues, however are split approximately 50-50.
FAQ
What are the possibilities for new technologies to combat climate change?
The possibilities of new technologies for addressing this global challenge are endless. Advanced science is making it possible to shift to a more sustainable world.
For lowering greenhouse gas levels, there are new carbon capture and sequestration methods. In addition to reducing emissions from livestock and soil degrading, enhanced agricultural practices can help reduce them. Smart grid technology can be combined with existing power infrastructure to increase efficiency. Additionally, improved building design can reduce energy consumption.
A new generation of synthetic biology techniques allows scientists to develop organisms capable of converting green fuels such as the CO2 laser into biofuel or other feedstock. This could make transportation more efficient if the market moves away from petrol-powered vehicles and towards zero-emission electric cars that are powered by clean energy.
Finally, increasing investment in digital tech and AI can enable people to access data across borders and help them make more informed consumption decisions. Ultimately, understanding our role in carbon production is paramount allowing us all to be better stewards of our planet.
What causes climate change?
Climate change has become a global problem due to an increase in human-generated greenhouse emissions. These gases are mostly emitted by fossil fuel combustion for electricity and transportation. These emissions lead to a greater amount of sun's energy being trapped in Earth’s atmosphere, which results in rising temperatures.
Climate change is also caused by other factors, such as population growth and land clearing. This further reduces the number of naturally occurring carbon sinks that absorb CO2 from the atmosphere. Climate change can also come from natural forces, such as changes in solar energy.
This combination of human activities results in Earth exceeding its ability to balance its energy budget. The result is an average global increase of 1° Celsius since pre-industrial days. Glaciers melt quicker than they form, and sea levels rise because oceans absorb most the heat energy. Other negative consequences include water scarcity, droughts and extreme weather events like flooding and hurricanes.
To avoid further damage, it is crucial that we reduce carbon emissions and take steps to curb our emissions. This will give us a fighting chance against climate change's already serious impacts. It is crucial to reduce our dependence of fossil fuels for electricity generation and invest in renewable sources, such as wind turbines/solar panels. These do not emit any harmful chemicals into the environment. Other sustainable practices like reforestation can also help restore some balance around these delicate planetary cycles we rely on for survival.
What does the role of greenhouse gases contribute to climate change?
Climate change is influenced by greenhouse gases. They act as an invisible blanket that wraps around the Earth, trapping heat radiation and warming it. Without them, the Earth would be much colder today than it is today.
The human activity of burning fossil fuels, or other industries that generate emissions, can create greenhouse gases. These activities will continue to increase heat trapping in the atmosphere. This will lead to increasing temperatures and extreme weather conditions.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most common greenhouse gas. It is produced when fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas are burned. Other major contributors to climate changes include methane, nitrous oxide and fluorinated gases (F-gases).
Because of human activities, the concentrations of greenhouse gases have increased substantially since preindustrial days. Global warming has resulted in an increase of temperatures around the world and in our oceans. It is also causing changes such as more intense storms and droughts, melting glaciers, and rising sea levels.
To avoid more damage from climate changes, humans must reduce their emissions by switching away from fossil energy to increase their use of renewable energy like solar and wind power. We can also adopt reforestation methods or agricultural methods that allow the soil absorb more CO2 in the air. These actions will help reduce atmospheric concentrations in greenhouse gases and create a healthier ecosystem for all life.
What is climate Change and how does this happen?
Climate change refers the long-term shifts that occur in global weather patterns due to an increase in greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, causing global temperatures to rise which leads to an array of changes in weather and climate. These can include rising sea level, melting glaciers or droughts, widespread coral bleaching, species extinction and disruptions in food production.
Human activity is the major cause of climate change. When these activities release massive amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere it warms the planet at a much faster rate than natural processes like volcanic eruptions as these activities produce many times more emissions than volcanoes.
Global greenhouse gas emissions are also influenced by deforestation, which contributes about 15-20%. When trees are cut down or burned it releases their stored carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. Furthermore, forests act like a natural carbon sink and remove CO2 from air. Without this absorption capacity carbon dioxide levels will continue rising with devastating consequences to ecosystems all over the world.
Other than CO2, human-caused pollutants also release other dangerous gases such as methane and nitrous oxide (N2O) into the atmosphere. Industrial processes have used methane extensively and it contributes to significant atmospheric warming. However, N2O is emitted mostly by agricultural soil management activities such as fertilization and tilling. These activities release excessive nitrogen into the soil which leads to N2O production when microbial contact occurs.
To limit climate change, we must collaborate across economic, political, and social institutions in order to reduce our emissions and transition away fossil fuel dependence towards renewable energy sources. The smart solution to reduce CO2 accumulation and atmospheric pollution could be replacing polluting fossil energy sources with zero-waste solutions. It is possible to reduce our environmental footprint by taking responsibility. Conservation measures such as reforestation can help protect biodiversity and absorb large amounts of CO2 into the environment. This will be a powerful tool in helping to solve the climate crisis and restore balance for future generations.
Statistics
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to make your house more energy efficient and combat climate change
You can make your home more efficient and reduce your carbon footprint. It will also save you money on your utility bills.
Make sure your home is well insulated and sealed. Check that windows and doors are properly fitted. Add weather stripping to any drafts and seal any gaps between the window frames and door frames.
Insulate your ceilings, floors, and walls to increase energy efficiency. You should inspect your attic and other areas for leaks.
Lighting can account for as much as 18% of household electricity consumption. Make sure to switch to LED bulbs, which consume up to 80% less electricity compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. You can also save money by installing motion sensors and timers to turn off lights when they are not needed.
The cost of replacing an old furnace or boiler can be reduced dramatically by using newer models that are more efficient. A programmable thermostat can be used to set temperature settings based on the time people are at home and away.
All windows should be replaced by double-glazed units that are more energy efficient and less heat escaping. Low-flow showerheads, which are low in water consumption, can be bought. They maintain an adequate pressure level and reduce water usage.
ENERGY STAR rated items can be used to replace appliances that consume up to 50% less power than noncertified models. Don't forget about small details such as unplugging electronic devices like phone chargers or TV boxes when not in use - this could save you a significant amount of energy over time!
These simple steps can reduce your impact on the climate and help you live more efficiently at home.