The fifth assessment of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), made waves this year. One of the most significant aspects of this report, was that it was first time the global community had shared the same view. It was the first ever joint meeting of the delegate. This was for many the first time that they had left their offices. After a short discussion on the future climate change, the delegates agreed that a new framework would be used to help guide the conversation toward a more collaborative approach. While no concrete plans were in place to make these changes, the participants took comfort in knowing that the previous meeting would set the groundwork for a more ambitious, flexible future for the countries most climate-tolerant. It is now hoped that the next round of high-level talks will produce even more effective results. With the release of the most recent report, a new era of environmental and social policy has begun. That said, this is still a tough task to manage.
FAQ
What is the impact of land use change and deforestation on climate change?
Deforestation and land use change have a direct and immediate impact on the climate. If trees are cut down, or burned, carbon dioxide, one the most important greenhouse gases, is no longer absorbed. Therefore, when trees are cleared by deforestation or burned for agricultural purposes, less carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere.
Changes in land usage can also cause more greenhouse gasses to be released into the atmosphere. For example, when forests are replaced with agricultural lands for livestock production, fertilizer, and pesticide use may increase emissions of nitrous oxide and methane. In addition, clearing can increase exposure to soils that contain large amounts of stored carbon; when these soils are turned over or disturbed by farming activities, they release additional carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
The impacts of deforestation and land-use change extend beyond just increased greenhouse gas emissions; it can also have an impact on regional air quality. The smoke from deforestation's burning events has been linked to poor visibility and other health concerns, such as asthma or other respiratory diseases. The global climate can change as a result of changes in local air quality. This is because more sunlight reaches the Earth's surface than the atmosphere.
Deforestation and changes in land use have contributed significantly to the increase in global greenhouse gas emissions. They also have had adverse effects on local air quality, which further contributes to climate change. If serious efforts to mitigate climate change are to be made, it is important that these practices are reduced.
What role can the energy sector play in climate changes?
It is crucial that the energy sector plays a significant role in climate change. Global warming is caused by the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This traps heat and causes an increase in Earth's average temperature.
This requires energy sources to move away from carbon emitting sources like natural gas and coal, and instead shift towards renewable energy sources, such solar, wind, or geothermal. This change can be made by government policy, incentives, and investments in innovative technology, such as hydrogen fuel cells. Businesses and households can reduce their carbon emissions by investing in infrastructure to support the use of renewable energy sources.
Other options include switching away from petroleum-fueled cars, moving towards electric vehicles, and public transport. Governments have the power to encourage and support investment in cleaner modes for transportation.
Additionally, companies must implement green business practices within their operations to reduce overall carbon footprints by implementing better insulation systems for offices or implementing energy efficiency plans for production facilities. This can dramatically reduce operational costs, while improving environmental performance metrics.
These initiatives must be championed not just at the company level but also at the government level for them to be truly effective; increasing taxes on pollution products encourages individuals to switch away from harmful practices without forcing them financially outcompeting polluters by providing vouchers or subsidies for low-carbon products will create an ongoing market to support sustainability efforts moving forward. The private and public sector must work together to combat climate change. Providing vouchers or subsidies for low-carbon products and switching to cleaner energy sources will create a market that supports sustainability efforts.
What are the causes of climate change?
Climate change is a global phenomenon that has been driven by an increase in human-generated greenhouse gases emitted into our atmosphere, primarily due to fossil fuel burning for electricity and transportation. These emissions lead to a greater amount of sun's energy being trapped in Earth’s atmosphere, which results in rising temperatures.
Other contributing factors to climate change are population growth, land clearance and destruction of ecosystems as well as deforestation, energy use, over-grazing and energy consumption. This decreases the amount naturally occurring carbon sinks that absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Climate change may also be caused by natural factors such as changes to solar radiation.
This combination of human activities results in Earth exceeding its ability to balance its energy budget. The result is an average global increase of 1° Celsius since pre-industrial days. Because oceans absorb the majority of heat energy, glaciers are more likely to melt than they ever form. Other negative consequences include water scarcity, droughts and extreme weather events like flooding and hurricanes.
To avoid further damage, it is crucial that we reduce carbon emissions and take steps to curb our emissions. This will give us a fighting chance against climate change's already serious impacts. Reducing our dependence on fossil fuels for electricity production is crucial alongside investing in renewable sources - think wind turbines or solar panels - which do not emit any harmful pollutants into the environment. You can also restore some balance in these delicate cycles of the planets that sustain us, such as reforestation.
How can developing countries and communities cope with the effects of climate changes?
Because of their limited access and lack of technology and healthcare, the impact climate change has on developing countries and communities is particularly severe. Climate change can increase the pressure on already limited resources. Floods and droughts can also cause damage to already fragile ecosystems. Rising temperatures can lead to a decrease in crop yields, which will disproportionately affect poorer communities struggling with food insecurity. Extreme weather events like heatwaves or hurricanes can lead to destruction of infrastructure, displacement of people and further perpetuating economic inequality.
Long-term consequences of climate change include increased resource scarcity and poverty as well as health effects such as an increase in vector-borne diseases like malaria or dengue fever. In addition, there will be a higher risk of flooding due to rising sea levels coupled with extreme weather events putting lives at risk in coastal areas where populations often lack the adequate infrastructure or emergency services needed for evacuation. To build resilience against these risks, mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions is necessary. Other measures include improved management and better access to water resources.
What are the implications of climate change for the environment and society?
The environment and society are both affected by climate change. Rising global temperatures, extreme weather events, sea level rise, and decreased air quality are just some of the environmental impacts of climate change. These changes can have serious implications for human populations, creating instability in communities, intensifying poverty and insect-borne diseases, altering human migration patterns, and destroying vital habitats.
Already, climate disruption is already having profound impacts on the environment and society around the world. This is expected to get worse as global temperatures continue rising.
Ocean levels rising due to melting ice caps is one of the most pervasive effects of climate change worldwide. This can lead to shoreline erosion and increased flood risk for coastal communities. Also, saltwater intrusion occurs, which negatively affects freshwater supplies in coastal areas in many countries.
As a result, extreme weather events such heatwaves or droughts are common in many countries. These events result in mass destruction of homes or businesses and can lead to relocation or complete loss of life. Extreme storms also present risks of flooding or landslides which can cause further damage to infrastructure, such as roads and railways.
Wildfires caused by climate change also increasingly occur more frequently than they did before with devastating results both for habitats and people living nearby who may find their lives at risk due to poor air quality when these fires spread smoke across affected areas.
These drastic changes often lead to displacement or refugee crises. People move out of their homes involuntarily or voluntarily when their communities become unsafe or uninhabitable due to the altered climate.
Increased aridity also increases dust storms worldwide with unhealthy air pollution caused by these making it difficult for people who suffer from respiratory illnesses such as asthma especially vulnerable. The possibility of pest infestations increasing is linked to increased temperature extremes, a phenomenon known "greenhouse bug". This further impacts global food insecurity. A smaller number of crops with lower nutritional quality could lead to additional hardships for those already struggling to make ends met.
What is the potential for new technologies to address climate change?
There are many technologies that can be used to tackle this global problem. The advancements in applied science allow us to make a transition to a sustainable future.
New methods of carbon capture and sequestration can be employed to draw down greenhouse gas levels, while enhanced agricultural practices can reduce emissions from livestock and soil degradation. Smart grid technology can also be used with existing power infrastructure for an efficiency boost, and improved building design can help minimize energy consumption.
Additionally, scientists can develop organisms using cutting-edge synthetic biological approaches to convert green sources of fuel like CO2 lasers into usable biofuels or alternate feedstocks. This could make transportation more efficient if the market moves away from petrol-powered vehicles and towards zero-emission electric cars that are powered by clean energy.
Finally, increased investments in digital technology or AI can provide people with more information on their ecological footprints across borders. This will allow them to make more informed decisions regarding their consumption habits. Understanding our contribution to carbon production is crucial for us all to be better stewards.
What is climate Change and how does this happen?
Climate change refers to the long-term shifts in global weather patterns that are caused by an increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, causing global temperatures to rise which leads to an array of changes in weather and climate. This can include rising sea levels, melting glaciers, extreme storms and droughts, widespread coral reef bleaching, species extinction, and disruptions to food production.
Climate change is caused primarily by human activity. These include burning fossil fuels, transporting electricity, cutting down trees, and farming livestock. These activities cause the atmosphere to heat up much faster than natural processes, like volcanic eruptions. They also emit many times more carbon dioxide than volcanoes.
A large part of the global greenhouse gases emissions is also caused by deforestation. Trees are destroyed or burned to release their carbon dioxide. Forests also act as a natural carbon sink, removing CO2 from the atmosphere; without this absorption capacity, carbon dioxide levels around the globe will continue to rise, with disastrous consequences for ecosystems.
The release of CO2 into the atmosphere is not the only effect of human-caused polluting. Other harmful gasses like methane, CH4, and nitrous dioxide (N2O), are also emitted by humans. Industrial processes have used methane extensively and it contributes to significant atmospheric warming. However, N2O is emitted mostly by agricultural soil management activities such as fertilization and tilling. These activities release excessive nitrogen into the soil which leads to N2O production when microbial contact occurs.
To minimize climate change humanity must make concerted efforts across social, economic, and political institutions to reduce these emissions drastically and transition away from our dependence on fossil fuels towards renewable energy sources such as solar, wind power, or low-carbon hydrogen fuels. The smart solution to reduce CO2 accumulation and atmospheric pollution could be replacing polluting fossil energy sources with zero-waste solutions. It is possible to reduce our environmental footprint by taking responsibility. Conservation measures such as reforestation can help protect biodiversity and absorb large amounts of CO2 into the environment. This will be a powerful tool in helping to solve the climate crisis and restore balance for future generations.
Statistics
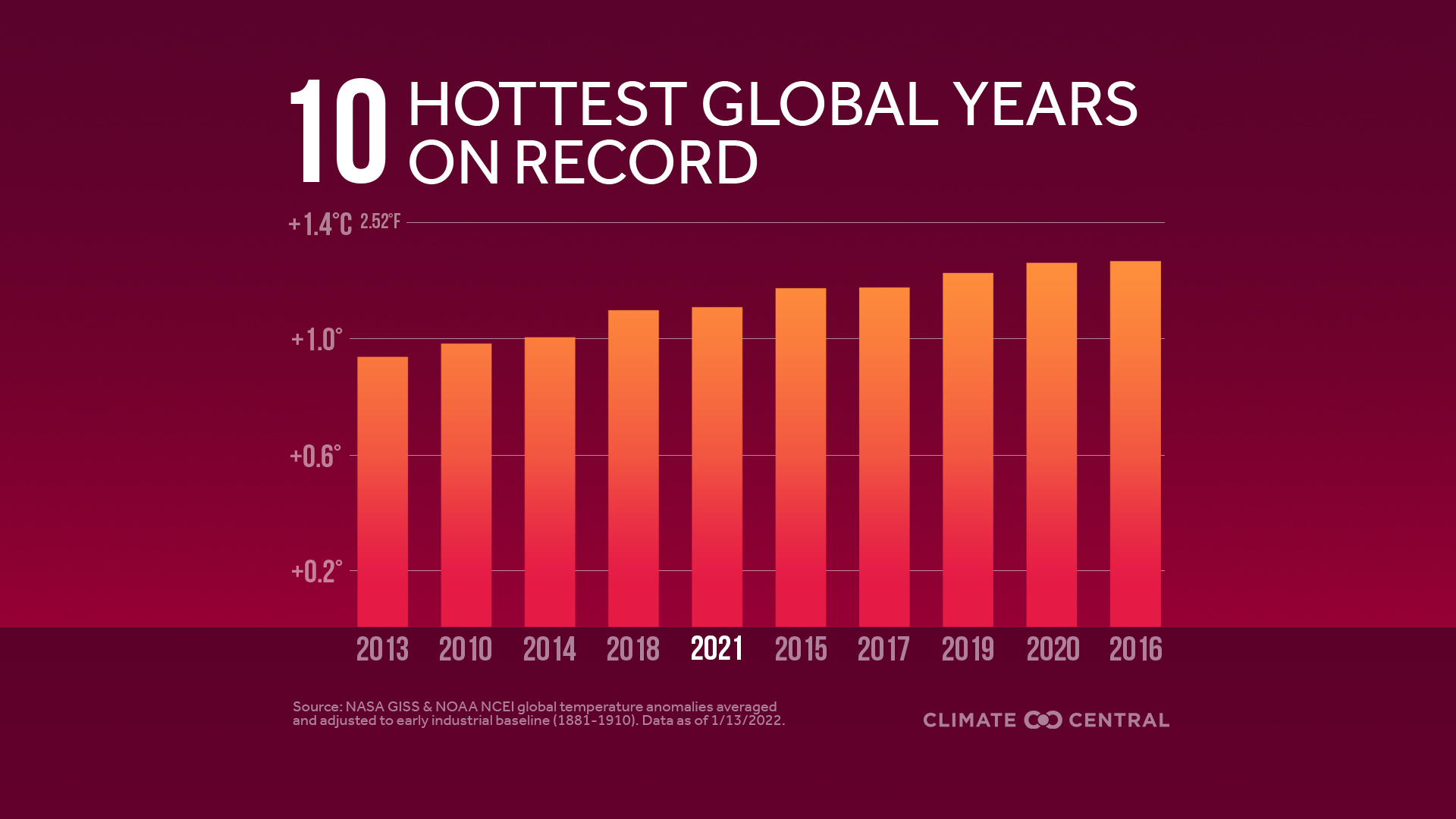
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to integrate sustainable practices into your everyday life to fight climate change
Reduce your consumption of food, energy, and clothing is one way to incorporate sustainability into your everyday life. Try shopping secondhand, borrowing from family and friends, or buying new items every other day. In order to reduce the amount methane in the atmosphere, it is a good idea to eat vegetarian meals only once or twice per week. Turn off lights whenever you are leaving a room in order to conserve energy.
The other way to combat climate changes is to reduce carbon emissions from transportation such as cars and aircrafts. Renewable power sources, such as solar panels, can be used to replace traditional fossil fuels. For climate action to be effective, it is essential that we support policy measures that promote clean air regulations. Finally, engaging with others around issues like ending plastic pollution and deforestation is hugely beneficial since it creates more conscious citizens who will act upon their knowledge!