Climate change impacts on human health are expected to increase, with more severe weather events, warmer temperatures, increased exposure to waterborne illnesses, and changes in disease-causing insects. It is vital for citizens to be informed about the health hazards climate change presents, and to plan for them.
Many health issues can be affected by climate change, including respiratory diseases, foodborne illnesses, and vector-borne disease. Climate change may increase the chance of large fires in certain areas of the world such as the West. Also, people are more vulnerable to asthma and allergic reactions.
Heatwaves are among the most serious climate-related threats to human health. Studies have shown that more frequent heat waves can lead to more heat-related deaths and complications for the heart and respiratory system. People who work outdoors are at greater risk.

Heat-related diseases are not the only danger. People also may be exposed to extreme events like floods, storms and tornadoes. These events may contaminate water with bacteria or other harmful chemicals. Also, they may cause food-borne illnesses, such as cholera, which can lead to dehydration and severe diarrhea.
Climate change will, among other effects, make air pollution worse. When fossil fuels are burned, it is expected that smog and ground level ozone will rise. These pollutants can worsen allergies, heart disease, and other respiratory problems.
Indirect effects of climate changes can have a negative impact on human health. They include the occurrences of infectious diseases like West Nile virus, cholera, and malaria. The incidence of seasonal allergies can increase with changes in pollen levels and ragweed. Storms that are more intense and frequent will cause havoc on land and water.
Vulnerable communities include babies, children, pregnant and elderly women as well as infants, children, older adults and pregnant women. Their vulnerability to climate-related hazards depends on their locations as well as their health and medical status.
Indigenous Peoples of USA are among the most vulnerable. They live in poor, isolated communities. They are dependent on the environment for their sustenance.

Although a majority of Americans are aware of the threat of climate change, they aren't always thinking about how their own health is affected. Some of the most vulnerable groups include older adults, minorities, people with preexisting medical conditions, and persons with disabilities.
PAHO's Climate Change and Health Program was created to address the health consequences of climate change. This program is designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and promote climate change adaptation strategies that are health-oriented. PAHO plans to award tribal governments and territories awards for their efforts in preparing for and responding the health effects of climate change.
While different people are affected by climate change in different ways, it is clear that it will have a major impact on American health. It is estimated that the U.S. will experience thousands of premature mortality by the year 2025, with many more deaths globally. Climate-related adverse health effects will affect those in the most vulnerable groups.
FAQ
What are the impacts of climate change and global warming on agriculture and food security
Climate change and global warming have a direct impact on agriculture and food security. Climate change can alter rainfall patterns, temperatures, soil moisture levels and extreme weather. This can impact farming activities, reduce crop yields, or cause loss of agricultural diversity. Warmer temperatures can increase the spread of diseases or pests that can impact crops and can also lead to shifts in the areas suitable for agriculture production. This can result in higher costs for food production, and worsening hunger and nutrition around the world.
Rising sea levels present a new threat. They can inundate agricultural land in many coastal locations, leading to increased salinity in wetlands where important crops grow. The changing climate can also affect livestock production. High temperatures in summer months can decrease fertility rates in animals such as cattle, sheep, or goats. This can lead to lower milk yields that can increase food insecurity in communities.
The relationship between climate change and global warming is a complex one; however, efforts are being made to mitigate these results through adaptation strategies implemented by governments worldwide such as strategic investments in climate-smart agriculture (CSA). This means promoting sustainable methods, such as crop rotation and the preservation of native seed varieties. These strategies help prevent adverse effects from climate change or other environmental stressors. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
In order to ensure food safety in an ever-changing environment, farmers across the globe will need to use technologies that are more sensitive and adaptable to changing climates. There must be improvements made to existing infrastructure in order to take the appropriate actions when critical crop thresholds fall. This includes installing stable irrigation networks that provide adequate access water at times when it is difficult for farmers to grow crops. Collaboration between different stakeholders is needed to ensure that the quality nutrition guidelines are adhered to in all climates.
What is climate change and how does it occur?
Climate change refers the long-term shifts that occur in global weather patterns due to an increase in greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, which causes global temperatures rise. This leads to many changes in weather and climate. These can include rising sea level, melting glaciers or droughts, widespread coral bleaching, species extinction and disruptions in food production.
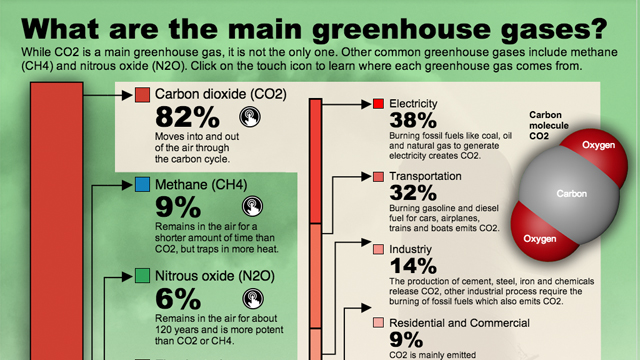
Human activity is the major cause of climate change. The planet is heated faster when these activities release large amounts carbon dioxide (CO2) than natural processes, such as volcanic eruptions. These activities also produce more CO2 than volcanoes.
Global greenhouse gas emissions are also influenced by deforestation, which contributes about 15-20%. When trees are cut down or burned it releases their stored carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. Additionally, forests act a natural carbon source that absorbs CO2 into the atmosphere. Without this capacity, carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere will continue to rise with devastating effects for ecosystems around world.
Not only does CO2 release into the atmosphere but it also releases other harmful gasses, such as methane(CH4) and nitrogen oxide (N2O). While methane is used extensively in industrial processes, it contributes substantially to atmospheric heating. N2O comes primarily from soil management activities like fertilization and tilling that release excess nitrogen into the soil. This leads to N2O being produced upon microbial interaction.
To reduce climate change, humanity must unite efforts across the political, social, and economic systems to reduce emissions dramatically and move away from our dependency on fossil fuels toward renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power or low-carbon hydrocarbon fuels. Replacing technologies that use polluting fossil fuels with smart solutions that promote zero-waste living could be an effective approach to decreasing atmospheric contamination while simultaneously reducing heating due to CO2 accumulation. It is possible to reduce our environmental footprint by taking responsibility. Conservation measures such as reforestation can help protect biodiversity and absorb large amounts of CO2 into the environment. This will be a powerful tool in helping to solve the climate crisis and restore balance for future generations.
What role does the energy sector play in climate change? How can this be addressed?
The role of the energy sector in climate change is immense. The main source of global warming comes from the burning of fossil energy. It releases carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, traps heat, and results in an increase on Earth's average temperature.
This is why energy sources need to shift away from carbon-emitting resources like coal and natural gas and instead switch towards renewable energy sources such as solar, wind and geothermal. This change can be made by government policy, incentives, and investments in innovative technology, such as hydrogen fuel cells. Businesses and households can reduce their carbon emissions by investing in infrastructure to support the use of renewable energy sources.
Alternatives include moving away from polluting vehicles like petrol-powered cars and moving to electric vehicles or public transportation. The government has great power to help societies transition away from oil-based infrastructures. They can support research into battery technology and encourage consumers to invest in cleaner modes.
To reduce carbon footprints, companies should adopt green business practices. For example, better insulation in offices and production facilities. This can dramatically reduce operational costs, while improving environmental performance metrics.
These initiatives should be championed at all levels, not just at company level but also at government. Raising taxes on pollution products encourages individuals and businesses to stop using harmful practices. While this may be a financial outlay for polluters, providing vouchers for or subsidy for low-carbon products can create a continuing market to support sustainability efforts. This is why tackling climate changes requires both private industry as well as private citizens to make a difference. By switching to green energy and adopting environmentally friendly practices, we can help to ensure that the future generations of people are affected positively.
Statistics
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to educate your community about climate change and mobilize action
Climate change education can take many forms - from online resources and interactive educational tools to classroom activities, simulations, and experiential learning programs. The key elements of effective climate change education are:
-
Practical knowledge of the subject is essential for people to be able to make informed decisions.
-
Showing how individuals can make an impact
-
Engaging participants in an open discussion about possible solutions
-
Shared experiences inspire action
By providing comprehensive climate change lessons for both students and adults alike, educators will be able to help their communities develop strategies for reducing their environmental footprint.
Furthermore, connecting scientific research to real-world examples is a great way to engage audiences in a meaningful conversation. The best practices and case studies can provide participants with the chance to experience positive outcomes firsthand. This can help them innovate or create replicable measures in their own communities.
Participants are empowered by incorporating action-oriented activities in educational curriculums. This gives them the mental tools needed to create campaigns, petitions, and take local actions. It also allows them to be agents for social and political change or sustainability improvement initiatives. Additionally, highlighting individual agency highlights the importance for participants in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and also showcases their collective contributions towards a bigger outcome. Additionally, involving stakeholders early on in policy-making efforts encourages active engagement in decision-making processes allowing them to become involved at all stages of the process which could result in more equitable outcomes for all parties affected by the policy design decisions. By combining our efforts to raise public awareness about the impact of climate change with appropriate actions to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions, we may be able create an environment in which these urgent matters are addressed with special attention where it is most needed. This will allow us to work together to implement successful measures that will help us achieve our collective goals.